Investment Thesis
Intel (NASDAQ:INTC) stock has plummeted by about 47% over the last three years. This underwhelming performance saw the stock trail its peers, some of whom registered strong double-digit growth. Despite a 40% drop from its December 2023 high, the current downtrend presents another great entry point for long-term investors.
Following our previous coverage and a 29% pullback, I’ve doubled down on Intel. The convergence of technical indicators highlights a strategic opportunity to establish or intensify long positions using dollar cost averaging (DCA). The best time to buy Intel was in December 2022, when we called the bottom as the stock approached its book value of $25.5.
Another good entry point has emerged following the current 40% pullback. Overall, $31 to $25 is the ideal entry range to create new or intensify existing long positions on the stock, following DCA to bring down the positional average near $25.
In today’s analysis, we will first explore the ugly side of Intel’s recent financial performance in the past few years, detailing the significant revenue and profitability decline since 2020. Then, we’ll balance this with the positive steps the company is taking to secure its future, including strategic investments and innovations in AI and internal foundry technology.
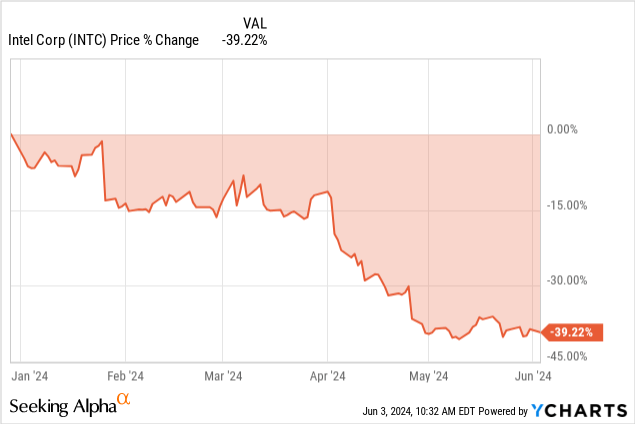
Targeting $40 by 2024 Amid Market Downtrend
Intel’s stock price is currently on a downtrend. It’s 40% down from its December 2023 high. Considering the price trend on a high-low basis (weekly time frame) over Fibonacci extension and retracement levels, the stock price may hit $33 as an average price target for 2024. Optimistically, the price may reverse to reach $40 by the end of the year. Pessimistically, following the current price trend, the stock may end up near $25.
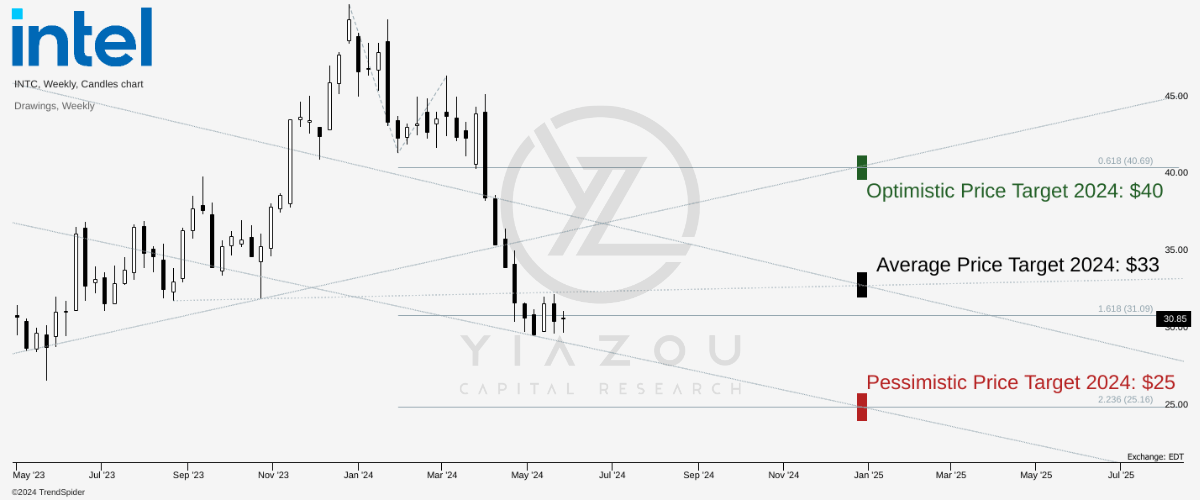
trendspider.com
Looking at the relative strength index – RSI, at 32, this signifies the current price consolidation as an ideal range to establish long positions as the indicator has recovered from below 30. On the other hand, the volume price trend (VPT) suggests a high intensity of bearish sentiment prevailing in the market. However, this is also a positive signal to be long on the stock as the indicator reverses after creating an inflection towards the yearly average.
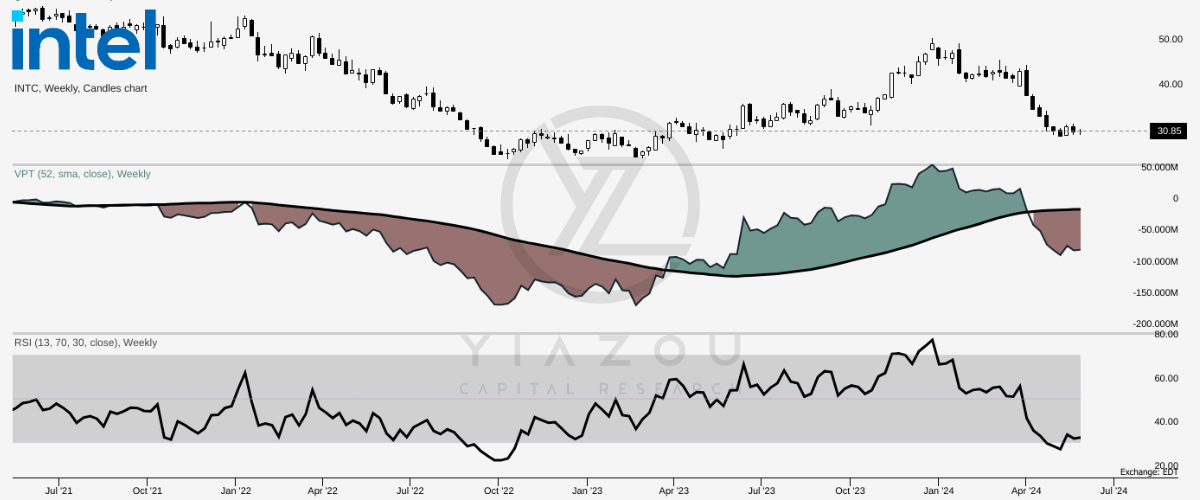
trendspider.com
Intel’s Financial Freefall: What’s Behind the Decline?
Intel’s financial performance indicators have been falling for the past couple of years. Since 2020, the bottom and top lines have been going south, which is not a good signal to investors. This has been transferred to the stock performance over the last three years.
This means a decline in the business revenue of $77.87 billion in 2020 to $54.23 billion attained in 2023, which evidences a drop in three-year CAGR revenue of -10.8%. Even more, its profitability also is strongly hit as its operating profit moves from $25.29 billion in 2020 to $4.67 billion in 2023, while its net margin falls from 26.84% in 2020 to 3.11% in 2023. Finally, its diluted EPS presents a 3-year CAGR decline of -40.15% due to its bad financial performance.
More important among them is that Intel’s relationship with Apple (AAPL) ended in 2020. However, even though it had lost the relationship with Apple, revenues dropped to around $50 billion, which means a significant customer exited, taking off something worthy of about $20 billion from the revenue stream.
The other reason behind this shaky financial performance is increasing competition, whereby competitors like AMD (AMD) and Samsung (OTCPK:SSNLF) have gained an impressive market share at the expense of Intel. And, of course, this is the continuing tech battle between the US and China, with all indications that China prevails.
Trade sanctions and tariffs between the two countries impose overwhelming resistance on Intel, as is evident by a 13% drop in its sales in China over 2023. This could worsen given that China has issued a directive that major telecom operators phase out foreign processors by 2027. This could be a major blow to Intel, given that China is its largest market, accounting for more than 27% of its total revenue.
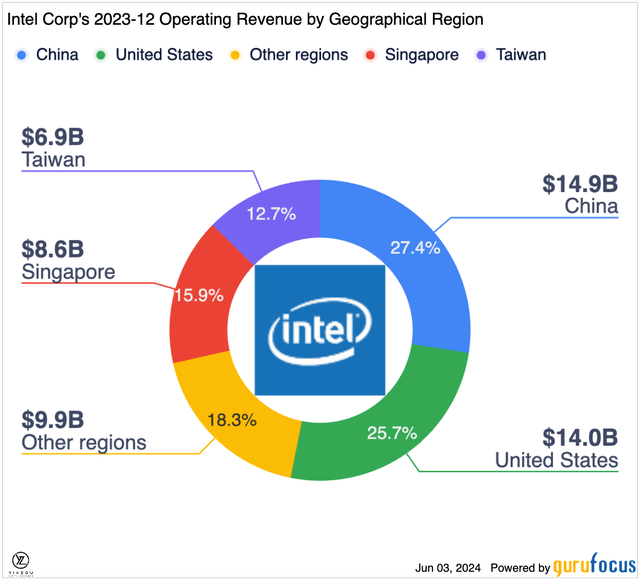
GuruFocus
Last but not least, the company faces patent lawsuits that could impact its financials and reputation if the verdict doesn’t favor it. The first case is the VLSI technology lawsuit, in which Intel has a $2.18 billion patent infringement award for VLSI technology. Alongside this case is the German injunction, where a regional court in Germany ruled that Intel infringed a patent on an R2 semiconductor, resulting in an injunction against sales of some Intel processors in Germany. The company is planning to appeal the case. The company plans to appeal the case, but losing could attract penalties, negatively impacting its financials and severely damaging its reputation, which may, in turn, affect consumer and investor confidence.
Intel’s Strategic Shift: Unlocking $10 Billion Savings and AI Dominance
In the wake of its financial struggles highlighted above, Intel is investing strategically to regain its success. First, the company has changed its business model to focus on internal foundry. Under the new model, the company is projecting to be more efficient and unlock its unrealized potential. It’s estimated that by 2025, Intel will save about $10 billion, which they believe will be possible because they have direct control over the manufacturing process.
Besides, the company also aims to realize potential underlying value in unrealized assets in capital, with its new model of targeting to leverage about $100 billion on investments and projects to enhance efficiency and profitability. This should be achieved with a 60% gross margin and 40% operating margin.
Besides the shift in business model, Intel has set its eyes on AI, the current tech industry wave. The company is building a multibillion-dollar AI accelerator business with a portfolio that includes the Gaudi family of chips. Last month, Intel unveiled its recent AI innovation, Gaudi 3.
The product outweighed Nvidia’s (NVDA) GPUs by approximately 50% in inference and about 40% in power efficiency. Intel aims to chop Nvidia’s 80% market share of AI chips. Although this innovation seems promising, it still lags behind Nvidia’s major innovations, such as the B200.
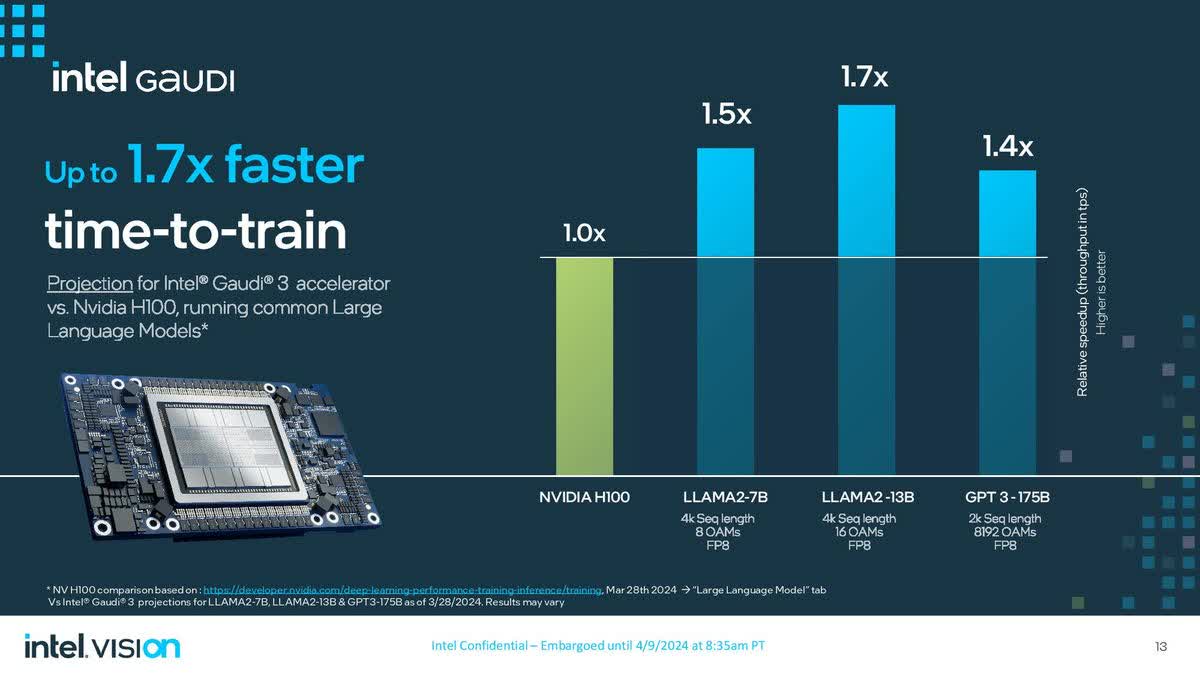
techovedas.com
According to precedence research, the AI Chip market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 29.72% between 2023 and 2032. This solid growth projection gives Intel tremendous growth opportunity, but for it to exploit it better, it has to move faster with its innovation to be at par or even beat competitors like Nvidia with new and unique products to claim a significant market share, which will then give its financials a major boost.
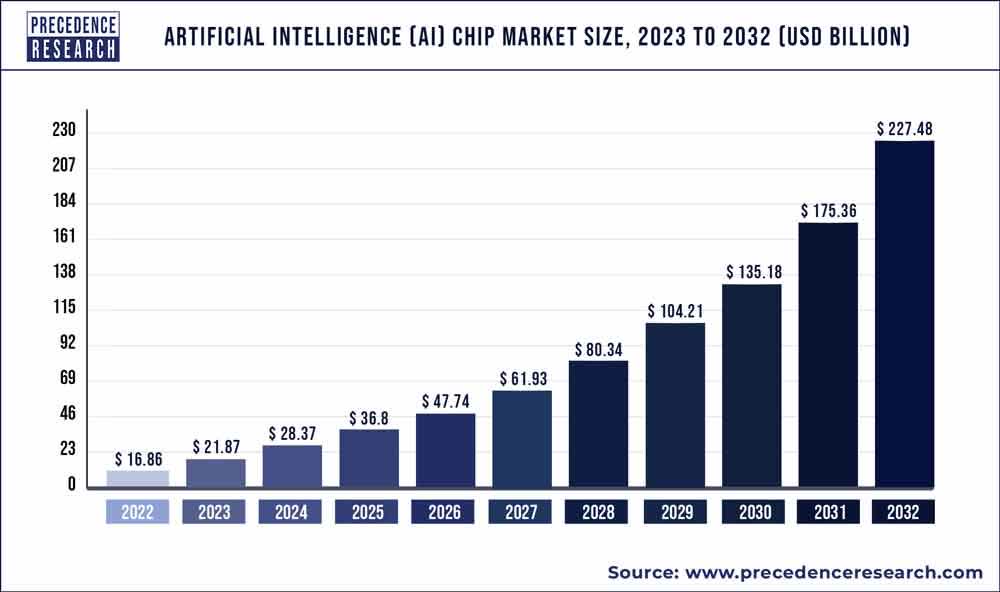
Precedence Research
Concluding Thoughts
Intel’s current market position reflects a challenging yet promising scenario. The giant’s strategic initiatives, including a $10 billion savings plan by 2025 and significant investments in AI technology, position it well for a robust recovery. The projected growth in the AI chip market, combined with Intel’s advancements in the Gaudi 3 chips, underscores the potential for substantial market share gains.
For investors, the key lies in timing. While the current pullback offers an attractive entry point, patience is crucial. Monitoring Intel’s financial performance and the impact of its strategic investments will be essential. In essence, Intel’s journey ahead holds promise, making it a valuable turnaround player in the AI era.
Editor’s Note: This article discusses one or more securities that do not trade on a major U.S. exchange. Please be aware of the risks associated with these stocks.
Read the full article here













